Job Queues
This tab shows the Job queues defined on the AMT-COBOL environment. Displayed are the name of the Job queue, the Applications that use the queue and the Batch Controller that uses the queue.
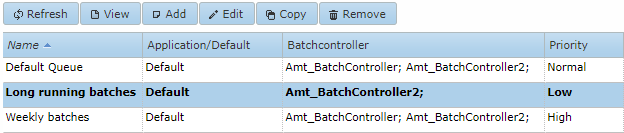
There should always be a default Job queue for jobs which are entered without a queue set. When a jobrequest is added without a queue set it will be placed in the default queue belonging to the application the job belongs to. In case there is no default queue for that application it will be placed in the general default queue.
When the list of Job queues is right clicked drop down list is presented with the possibility to view the job queues details, to add a job queue, to change a job queue or to remove a job queue.
Selecting Add, Edit or Copy a Job queue will open the following popup window. In case of Add with empty edit boxes.
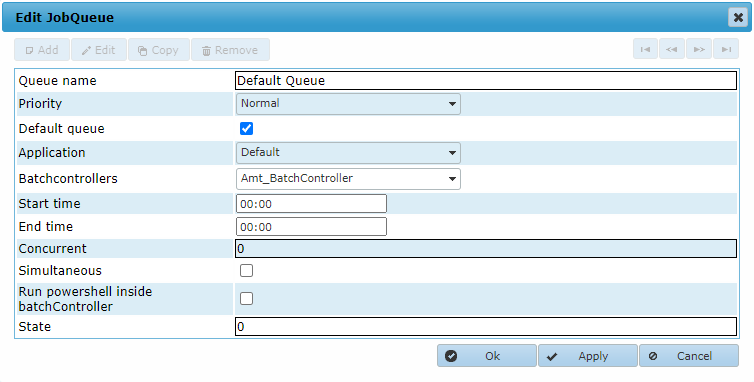
- Queue name: The name of the queue can be defined.
- Priority: Priority qualification of the Job queue. Can be set to High, Normal or Low. Jobs placed in a queue with a higher priority will take precedence over jobs placed in a queue with a lower priority.
- Default queue: When this checkbox is checked this queue will be the default queue. There can be one default queue per application and one general default queue (application 'Default'). See also: Job Queue Priority.
- Application: The application that this queue is for. When set to Default it can serve all applications.
- Batchcontrollers: Selects the controllers to use for this queue by ticking the checkboxes in the dropdown menu. At least one needs to be selected. When more are selected, the batchcontroller which is first to look for a new jobrequest in the queue will get the jobrequest.
- Start time and End time: A time window can be set in which the jobs in the queue will be executed
- Concurrent: Sets the number of jobs that can be run at the same time from this queue. If set to zero there is no maximum.
- Simultaneous: If this is checked the batch controller may run more than one instance of the same report or batch at the same time.
- Run PowerShell inside BatchController: When this option is checked, PowerShell scripts will not run as a separate PowerShell process, but will run inside the process of the Batchcontroller in a separate thread. In scripts that take no longer then 4 seconds to run, this option will speed up performance considerably since the runtime libraries will not have to be loaded and no database connection needs to be created for each script. In order to be able to run PowerShell scripts inside the Batchcontroller both the environment and the scripts themselves must comply to a list of requirements and restrictions.
- State: Not used.
Changes applied will be used for all new jobrequests.
