Converted VSAM Files in Database
Converted VSAM files in Database are files that were converted from VSAM files to a database table during migration to AMT.
A VSAM table is a normal AMT table in the repository. A table option “VSAM file name” was added and this must contain the file name the table was converted from. The generator will generate extra code when VSAM file name has a value.
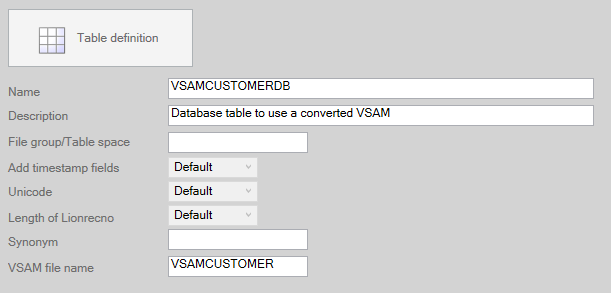
A VSAM table must have exactly one index. At migration this index was automatically created. Adding more indexes gives runtime errors because AMT does not know which index to use.
In order to avoid re-coding whole sections, these converted VSAM files make use of special AMT VSAMDB commands in exec blocks. These VSAMDB commands were created to mimic IBM CICS file handling commands as used with the original VSAM files. EXEC VSAMDB statements will only work for tables with a VSAM file name set.
Online
Available EXEC VSAMDB statements:
- READ
- WRITE
- REWRITE
- DELETE
- UNLOCK
- STARBR
- ENDBR
- READNEXT
- READPREV
The VSAMDB statements are identical to the CICS statement they replace. For example:
| Cics read: | VSAMDB read: |
| EXEC CICS READ DATASET('VSAMFILE2') INTO(WS-VSAM01) RIDFLD(WS-VSAM01-KEY) EQUAL END-EXEC. |
EXEC VSAMDB READ DATASET('VSAMFILE2') INTO(WS-VSAM01) RIDFLD(WS-VSAM01-KEY) EQUAL END-EXEC. |
VSAMDB supports the CICS parameters and error handling. See CICS documentation for details.
| Please note that when locking a record for update, writing a record or updating a record, this record will stay locked in the database until a commit has been performed. For example, this means that when using a READ statement with the UPDATE option, a subsequent UNLOCK statement will not unlock the record in the database. Locked records can be committed by executing EXEC CICS SYNCPOINT or ending the transaction. |
Batch
For batch programs, which do not support CICS commands, the regular COBOL file handling commands were translated to VSAMDB statements during conversion.
VSAMDB is added to ASSIGN in the SELECT statement of the File-control paragraph, the file definitions are kept original.
Example:
FILE-CONTROL.
SELECT VSAMFILE2 ASSIGN TO VSAMDB VSAMFILE2
ORGANIZATION IS INDEXED
ACCESS IS DYNAMIC
FILE STATUS IS IO-RETURN-CODE
RECORD KEY IS VSAM01-KEY.
The ASSIGN TO VSAMDB <filename> statement signals the generator that the file is a converted VSAM file, the filename is the name defined in the table.
Error handling like AT END and INVALID KEY is added to EXEC VSAMDB.
Example COBOL code before migration:
READ VSAMFILE2 NEXT INTO WS-VSAM01
AT END
MOVE 'READNEXT-1 AT END ERROR' TO WS-ERRORMESSAGE
PERFORM SETERROR
NOT AT END
ADD 1 TO WS-TEST-CNT
Example EXEC VSAM code after migration:
EXEC VSAMDB READNEXT
DATASET(VSAMFILE2)
INTO(WS-VSAM01)
AT END
MOVE 'READNEXT-1 AT END ERROR' TO WS-ERRORMESSAGE
PERFORM SETERROR
NOT AT END
ADD 1 TO WS-TEST-CNT
END-EXEC.
The following statements are translated:
| COBOL statement: | EXEC VSAMDB statement: |
| READ <file id> INTO <record> | READ FILE(<file id>) INTO(<record>) |
| READ <file id> NEXT [RECORD] INTO <record> | READNEXT FILE(<file id>) INTO(<record>) |
| START <file id> KEY >= <key> (only >= and = are supported) |
STARTBR FILE(<file id>) RIDFLD(<key>) GTEQ |
| WRITE <file layout> FROM <record> | WRITE FILE(<file id>) id, not layout FROM(<record>) |
| REWRITE <file layout> FROM <record> | WRITE FILE(<file id>) id, not layout FROM(<record>) |
| DELETE <file id> | DELETE FILE(<file id>) RIDFLD(<key>) added at conversion |
| OPEN <open mode> <file id> | OPEN MODE(<open mode>) FILE(<file id>) |
| CLOSE <file id> | CLOSE FILE(<file id>) |
As shown above, the EXEC VSAMDB statements have some extra features compared to EXEC CICS statements accessing VSAM files to support Cobol file statement behavior:
- It is possible to use [NOT] AT END and [NOT] INVALID KEY clauses in some of the statements.
- It is possible to specify a File Id in the FILE or DATASET parameter instead of a file name. The File Id must be specified in a SELECT with ASSIGN TO VSAMDB.
- READ, READNEXT, WRITE may be called without a RIDFLD parameter when a File Id is specified.
- READNEXT may be called without a previous STARTBR because READ NEXT is allowed without a START. In that case reading starts at the first record.
- OPEN with OUTPUT as open mode will truncate the table to emulate the creation of a new file in the original command.
- Other open modes and the CLOSE command will only reset the FILESTATUS variable to 0 (zero, successful).
General Remarks
Like VSAM files, the tables must be specified in the File Control Table. Name, file type (indexed), max record size and key length are used by EXEC VSAM commands.
