AMT Java Variables
Variables Class Structure
A graphical representation of the variables class structure is shown below.
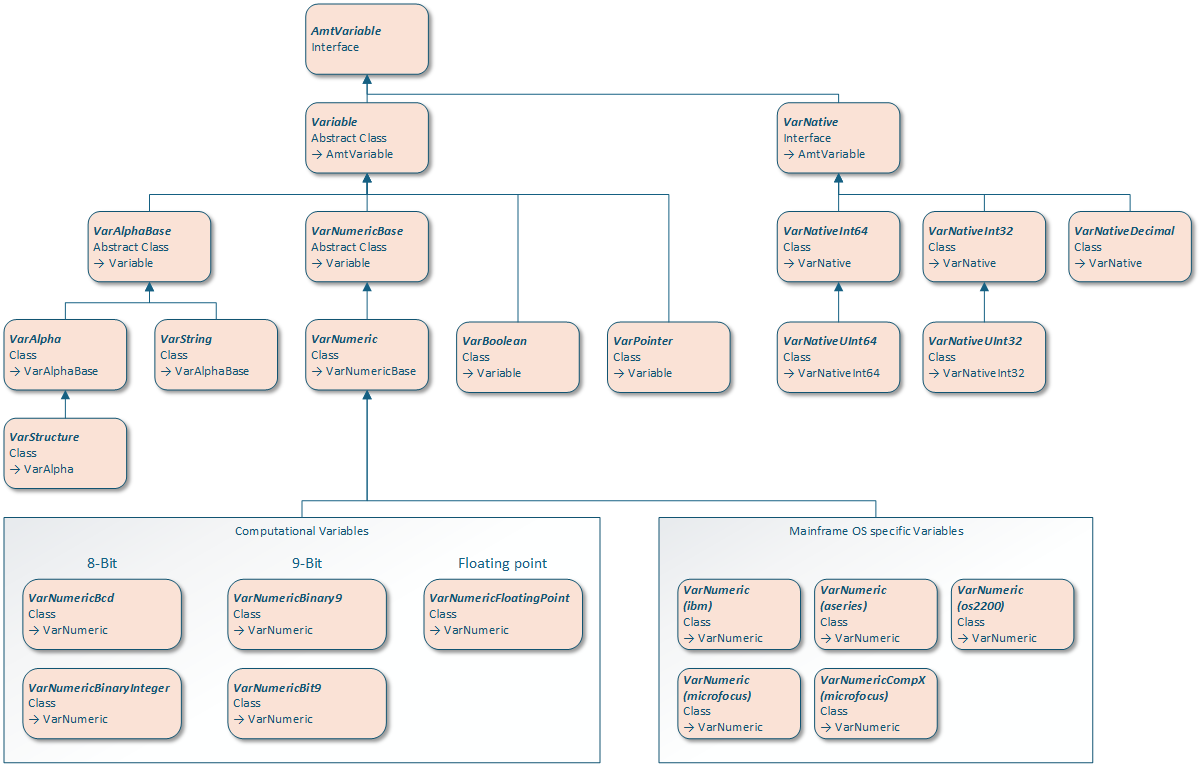
The Variable class can never be used directly. Four different classes are derived from this class:
- VarAlphaBase
- VarNumericBase
- VarBoolean
- VarPointer
The VarBoolean and VarPointer classes can be used directly in the code, the other two are base classes for three other classes which can be used in the code of programs and forms.
- VarAlpha
- VarString
- VarNumeric
The class VarStructure makes it possible to create structures of objects of the Var… classes.
Additional Variable Types
There are three more Variable types which are not a separate class but merely additional properties of the VarNumeric class:
- VarBaseNum.Signed
- Financial
- Currency
A normal VarNumeric can only hold positive numbers. A Signed can also hold negative numbers.
The Financial and Dollar Numeric types are only used at display time (in forms or prints) and influence the formatting.
Native Variable Types
Native variable types are lightweight variable types which do not use shared memory buffers or COBOL format emulation, but instead use the native variable types of the Java programming language. These variable types are only used in special situations where performance is critical.
Mainframe OS specific Variable types
Mainframe operating systems sometimes handle variables in such a way that mainframe specific variable types were designed in AMT.
At this moment this has only been necessary for Numerics on various mainframes resulting in the following classes:
- VarNumeric (ibm)
- VarNumeric (aseries)
- VarNumeric (os2200)
- VarNumeric (microfocus)
- VarNumericCompX (microfocus)
Computational
The implementation of COBOL Computational variables on AMT.
These are only to used in migrated code. When creating new variables it is very strongly advised to use only the normal VarNumeric or Mainframe specific numeric variables.
COBOL Computational variables differ from normal numeric variables in the way the numeric values are represented in memory. The usage in the code remains the same as for normal numeric variables except for the Bit9 with which bitwise operations are possible.
Another important difference is the Computationals for 8 bit machines like IBM mainframes and 9 bit machines like OS2200. Since the memory representation between 8 bit (byte) and 9 bit machines are not compatible the Computationals cannot be mixed in any way. The 8 bit mainframes lead to the numeric variables VarNumericBcd and VarNumericBinaryInteger and the 9 bit mainframes to VarNumericBinary9 and VarNumericBit9. Additionally there is a separate class for floating point variables: VarNumericFloatingPoint.
- VarNumericBcd
- VarNumericBinaryInteger
- VarNumericBinary9
- VarNumericBit9
- VarNumericFloatingPoint
