Nested Classes Web Services
The use of Classes in Web Services will be explained using the Class 'Car' and its member classes, which are already defined in the section "Nested Classes" on the "Usage of Classes" page.
Provided Web Service for nested classes
Provided Web Service Routine
As example the following Provided Web Service routine is created in a Web Service enabled Form:
begin_routine
if auto =NULL
auto := car.create ()
auto.engine := enginetype.create ()
auto.tires := tiretype.create ()
endif
auto.carbody := 'Hatchback'
auto.color := 'Progressive Black'
auto.engine.cylinders := 2
auto.engine.power := 63
auto.tires.width := 185
auto.tires.diameter := 15
end_routine
When no instance is passed to the routine a new one is created, then the field members are filled with new values and the result is available to the Provided Web Service through the as var defined parameter.
| Until AMT 84 'classes' and 'lists' as a routine result parameter were not supported for use with Provided Web
Services. Only 'classes' and 'lists' as var defined parameters were supported for use with Provided Web Services. With the release of AMT 84 both 'lists' and 'classes' are supported as routine results including for use with Provided Web Services. |
Creating the Provided Web Service
From this routine a new Provided Web Service can be created using the normal procedure as shown in the Web Services help pages. The resulting Operations view will look like the example below.
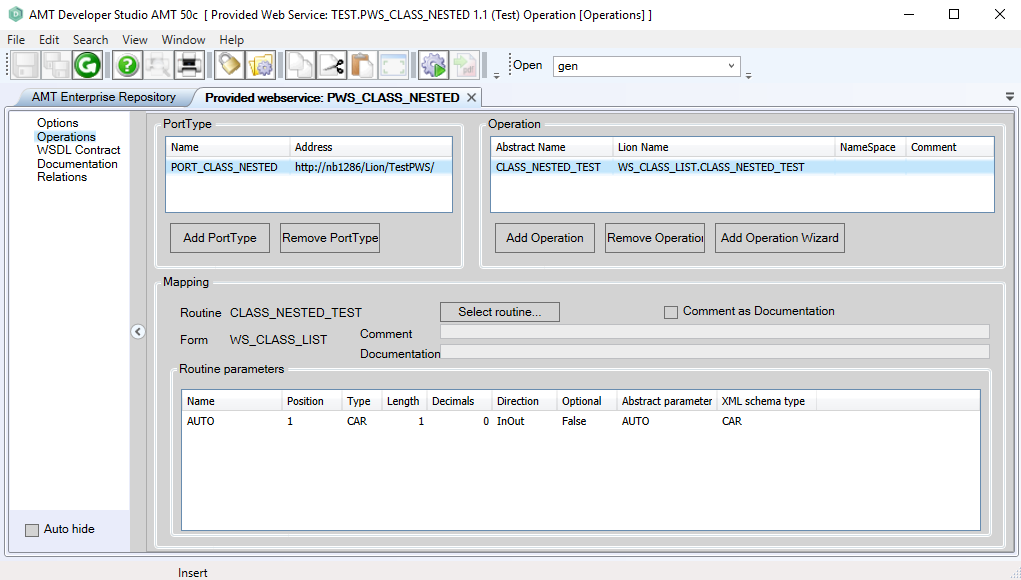
The returned type should be the Class type and the length will be 1. The Provided Web Service can now be generated and configured in the Provided Web Services web.config and the appropriate <PortType>.ini file.
Testing the Provided Web Service
The Provided Web Service can then be tested using Soap UI as shown below. Best is to import the WSDL into Soap UI using the Web Service itself. Because of the var usage in the Provide Web Service routine dummy input values are needed in the request.
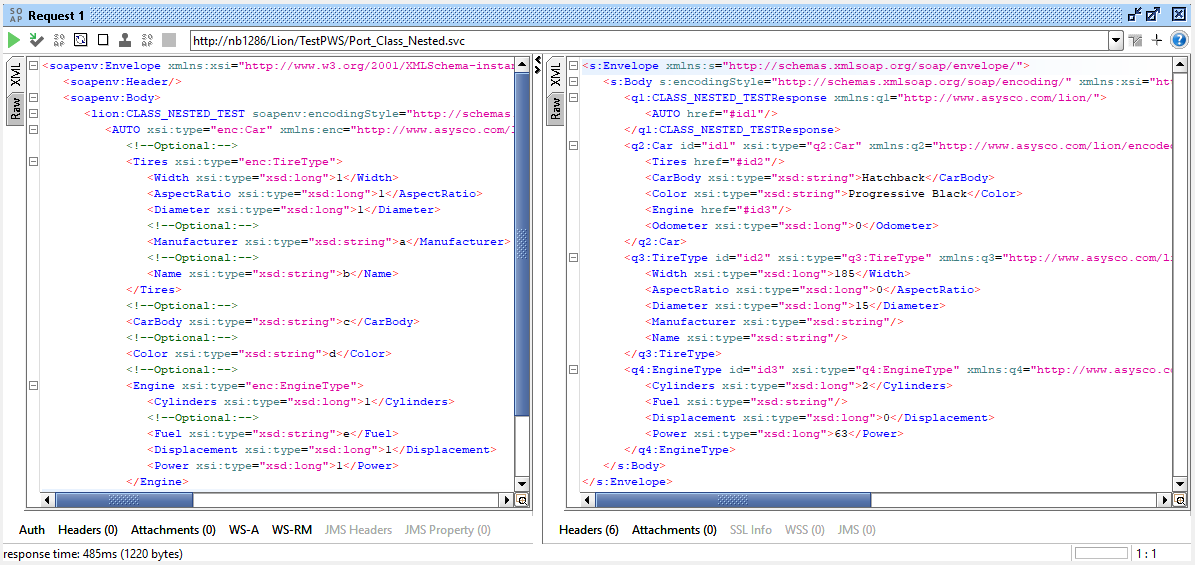
Returned are the Field members values from the Instance of the Class as shown above.
Consumable Web Service for nested classes
Creating the Consumable Web Service
For the consumable web service, the previously created nested class provided web service example will be used in the same way as shown in the Web Services help pages. The resulting Operations view will look like the example below.
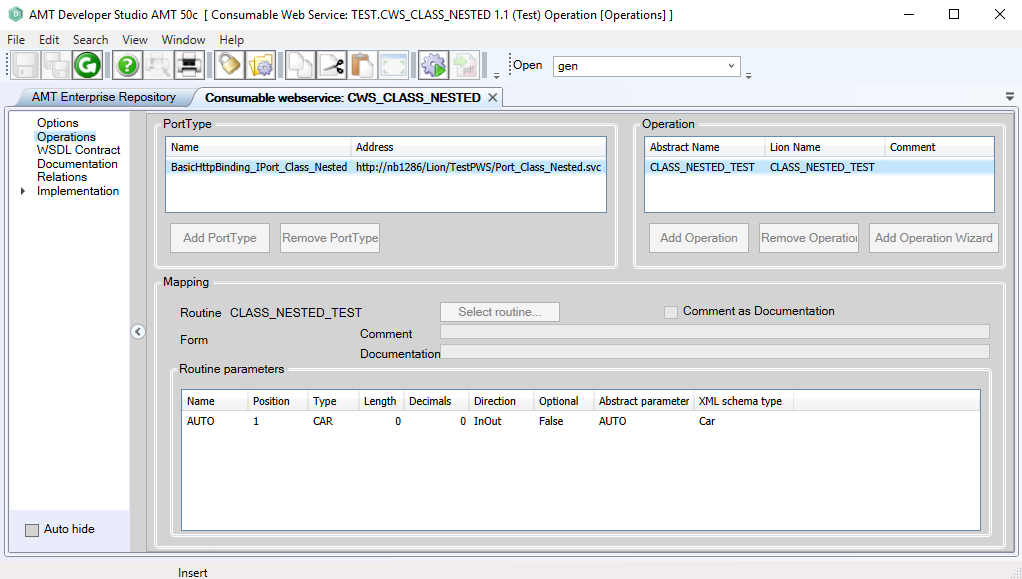
A new class type with the same name as the original will be created from the provided class. This is a local class definition with member classes in the Consumable Web Service object, which can be viewed in the Implementation > Definitions menu option.
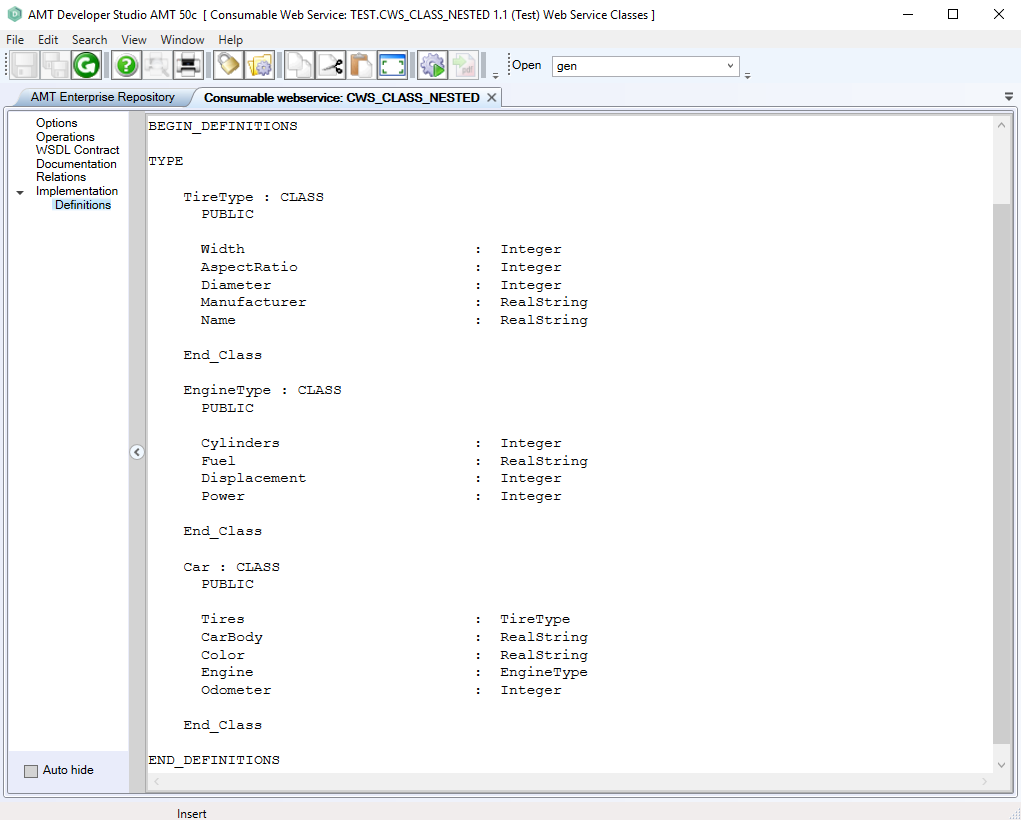
This local class can be used in other objects to create an instance of it, which can then be filled by a call to the consumable web service.
Consumable Web Service Report
In a report this could look like the following example:
const
var
fleetcar : cws_class_nested.car
booleans
end_definitions
routine main
begin_routine
fleetcar := cws_class_nested.car.create ()
fleetcar.engine := cws_class_nested.enginetype.create ()
fleetcar.tires := cws_class_nested.tiretype.create ()
cws_class_nested.basichttpbinding_iport_class_nested.class_nested_test ( fleetcar )
sme ( fleetcar.carbody, fleetcar.engine.power )
end_routine
First a variable (fleetcar) is defined as the local class of the consumable web service, then an instance of the class is created as well as instances of its member classes. This instance is used in the call to the consumable web service, which fills it with data from the provided form routine (see the top of this page).
